What are the Common Properties of Hydrocolloids?
Common Hydrocolloids Properties
Hydrocolloids can increase the viscosity of the system or form gels, sometimes also known as pastes, banyan gum, thickeners, edible gum. The basic properties of hydrocolloids include diffusion and Brownian motion, sedimentation phenomenon, osmotic pressure, optical properties, rheological properties, double electric layer around the limb mass, stabilization and flocculation, etc.

So,
what are the properties of hydrocolloids applied in food industry?
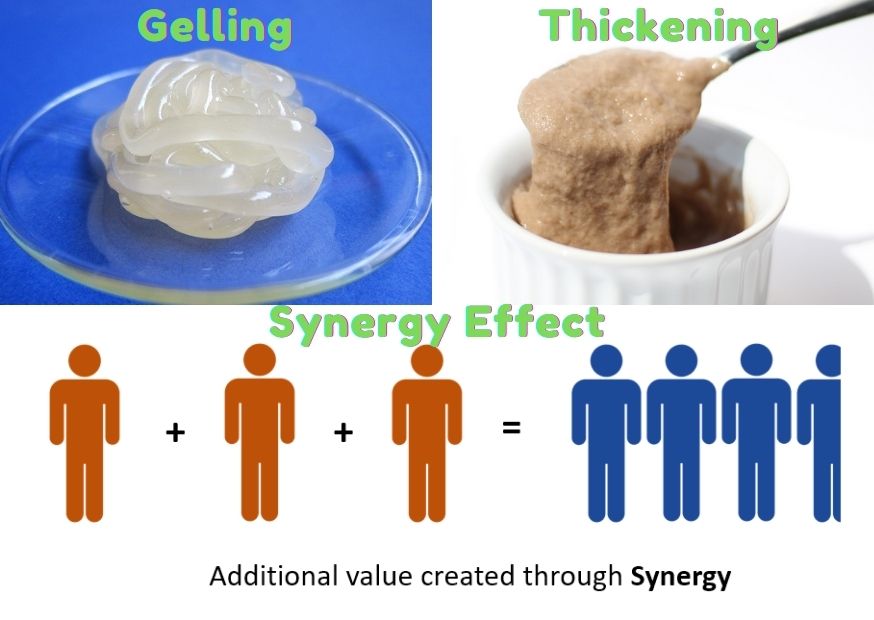
1. Function of Gelling
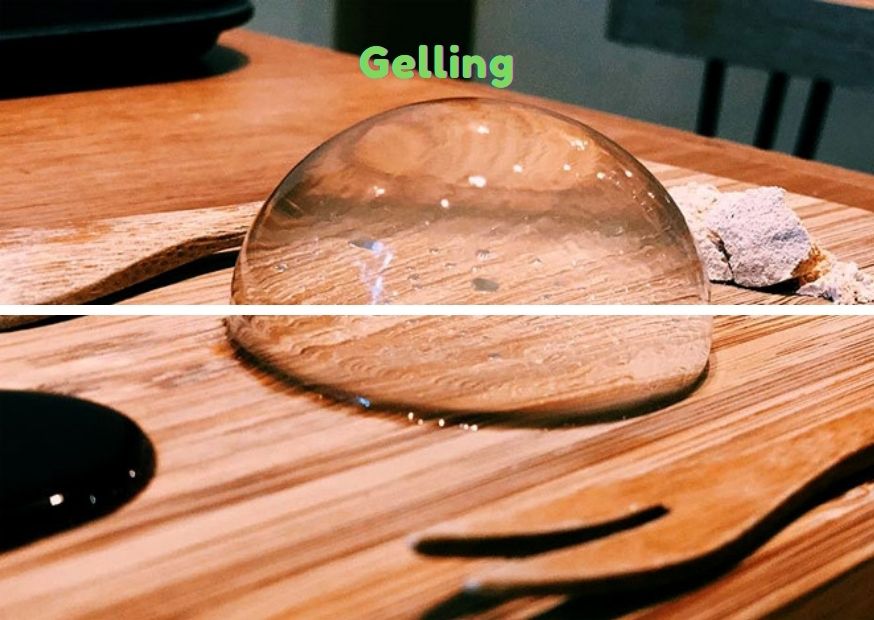

Some hydrocolloids can form gels at higher concentrations or under the conditions of external temperature, pH, ion concentration, etc.
Generally speaking, polysaccharides with more hydrophilic groups are easy to form gels. Polysaccharides with more branched chains are not easy to form gels because they are less affected by acids, bases and salts, but they can be complexed with other gums to form gels.
Anionic polysaccharides are easy to form gels in the presence of electrolytes, and usually electrolytes and chelating agents can be added to regulate the speed and strength of gel formation.
Hydrocolloid solution will be diluted by shear force such as squeezing and stirring, and the viscosity will be reduced, and hydrocolloid gel will be shaken or thixotropic under the effect of shear force.
As soon as the external force stops, the shaking or thinning solution can be frozen in the gel again.
2. Thickening Effect
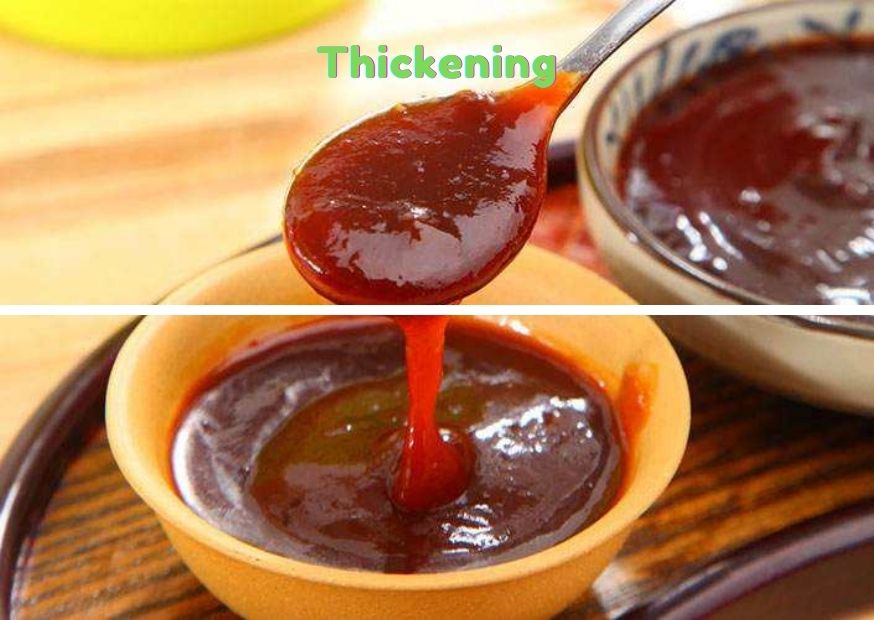

Hydrocolloids have a certain viscosity, with thickening effect, hydrocolloid molecules do not interact with each other after hydration.
Generally speaking, the hydrocolloids that can easily form a network structure in solution or have more hydrophilic groups have a higher viscosity. The same hydrocolloid, the greater the molecular weight, the greater the viscosity of the system with the same mass concentration.
As the concentration of hydrocolloids increases, the viscosity increases to a greater or lesser extent.
The viscosity of ionic hydrocolloids is more influenced by the electrolyte and pH of the system than that of non-ionic hydrocolloids.
For example, the viscosity of sodium alginate is stable at pH 5-10, and the initial viscosity increases significantly at pH less than 4.5, while the acid-catalyzed degradation of alginate molecules also occurs, and the viscosity gradually decreases. When the pH further decreases to 2-3, alginate precipitates and precipitates out, while the maximum viscosity of propylene glycol alginate appears at this time.
Polymers with more side chains (xanthan gum, propylene glycol alginate) have unique acid, alkaline and electrolyte resistance properties due to their special structures.
Other macromolecules with more side chains, such as propylene glycol alginate, have similar properties.
The viscosity of edible gum decreases when the temperature increases and increases when the temperature decreases. Many macromolecular substances undergo degradation at high temperatures, especially under acidic conditions, and a permanent decrease in viscosity occurs.
3. Synergy Effect
Some hydrocolloids show synergistic effects of thickening and gelation, such as carrageenan and locust bean gum; xanthan gum and locust bean gum; tragacanth gum and sodium alginate; tragacanth gum and xanthan gum.
The common features of these synergistic effects are.
When the solution is mixed and after a certain period of time, the viscosity of the system is greater than the sum of the viscosity of the components, or becomes a high strength gel after the gel forming.
For example, konjac gum compounded with other gums (such as xanthan gum, carrageenan, etc.) has an excellent synergistic effect, can make the viscosity of xanthan gum & carrageenan greatly increased.
A thickening agent compounded with Konjac powder and other gums (such as carrageenan, agar, CMC, xanthan gum, guar gum, locust bean gum, etc.), can be used in modulated milk and vegetable protein drinks to make the system stable and rich in taste.
Common Hydrocolloids Properties
Related Articles

We are a biotech company specializing in the research, development, and commercialization of innovative and technological food additives hydrocolloids Agar Agar, Carrageenan, and Tailor-Made Stabilizer Solutions.
With the extended know-how and experience in the research, application, and use of Hydrocolloids, we could provide one-stop-shop customized solutions perfectly matched to the needs of our customers.
Our products cover the needs of the Meat, Dairy, Bakery, Confectionery, and other industrial sectors.








