E406 Agar vs Agarose | Difference between Agar and Agarose
Agar vs Agarose | Table of Contents
Abstract: Agar vs Agarose. Agar is a hydrocolloid composed of agarose and agar pectin, and agarose can be obtained by removing agar pectin from agar. Agar and agarose have been widely used in food, medicine, chemical, textile, national defense and other fields because of the same special gelling properties, such as significant solidity, hysteresis and hysteresis, easy absorption of water, special stabilization effect, etc. They are called "novel East Asian products" in the international market.

1. What is Agar Agar

Agar has been used as a unique food additive in China for more than 300 years. Agar is a hydrocolloid composed of agarose and agar pectin, which is a seaweed gel extracted from red algae.
Agar has a wide range of applications, mainly in food industry, pharmaceutical industry, daily chemical industry, biological engineering and so on. In food production, agar not only can change the texture of food, but also can improve the grade of food.
Types of Agar

Agar Powder
Ordinary agar powder, instant agar
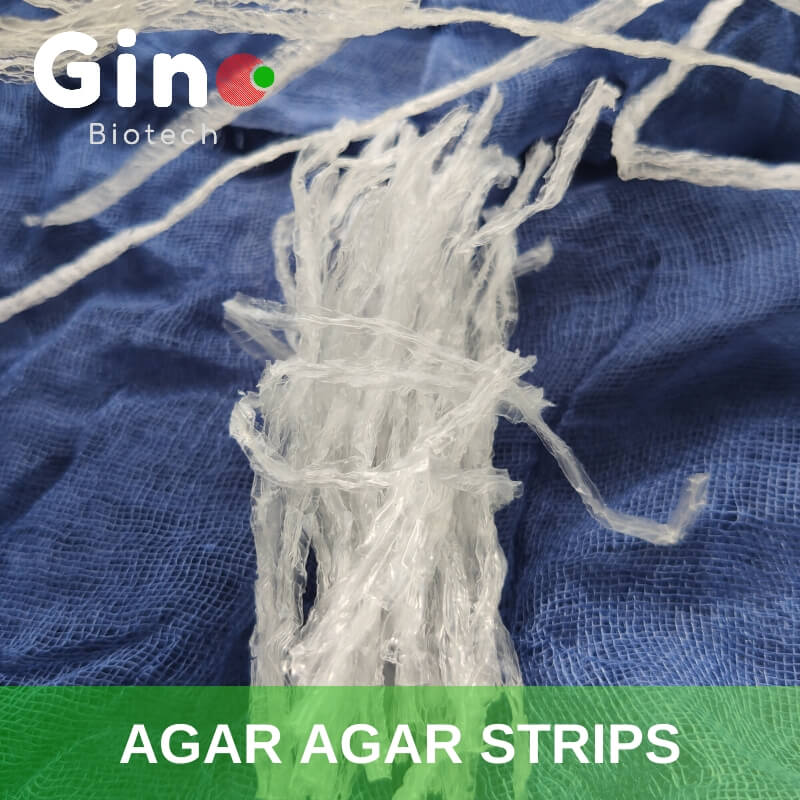

Agar Strips
Bulk packaging, Retail packaging

Agar Flakes
New forms of agar products
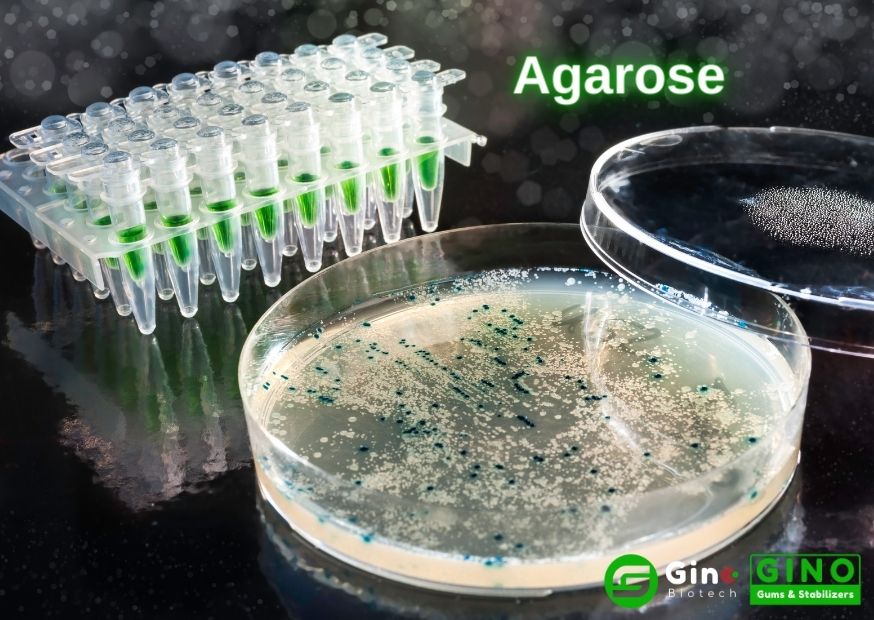

2.1 Introduction to Agarose
Simply put, when the agar pectin is removed from the agar, the remaining part is agarose. Agarose is a result of the purification of polysaccharide agar.
Agarose is a chain-like neutral polysaccharide composed of D-galactose and 3,6-endoether-L-galactose. The structural unit contains a hydroxyl functional group, which is easy to form hydrogen bonds with hydrogen atoms in the structural unit and water molecules around the chain segment.
2.2 Agarose Properties
- Good transparency: Fast dissolution, clear and transparent gel
- High strength: Ensure the strength and elasticity of the gel, and the gel is not easy to be broken even in low concentration.
- Low EEO(electroendosmosis): Reduce the influence on the migration and separation of electrophoretic mass migration
- Extremely low background: No other fluorescent substances interfere, the swim band and the background are clearly separated in black and white, and the pictures taken are good.
- No nucleases and proteases.
2.2 Agarose Properties
In addition to the same properties as agar, agarose also has higher purity, less electroosmosis, high gel strength, colorless, etc. It has been widely used in clinical testing, biochemical analysis, separation and purification of proteins, enzymes, nucleic acids, antigens, antibodies, viruses and polysaccharides, and preparation of advanced drugs.
2.4 Agarose Uses
Used as a biochemical reagent
Detailed Uses of Agarose
- For deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), lipoprotein and immunoelectrophoresis.
- Substrate for biochemical research such as immunodiffusion.
- Biology, immunology, biochemistry and microbiology research.
- Used in clinical medicine for hepatitis B antigen (HAA) determination.
- Blood electrophoresis analysis.
- A-fetoglobulin assay.
- Diagnosis of hepatitis, hepatocellular carcinoma and cardiovascular diseases.
- Agarose is also the main ingredient in the manufacture of capsule shells.
- It is also used in the manufacture of plasma substitutes and is often used as a stabilizer and emulsifier.
- Due to its good biocompatibility, it is also widely used in the production of biological separation media.

It is known that there are about a thousand uses of agar and agarose. Among them, agar is not only directly edible but also has a wide range of uses in the field of scientific research, industry and medicine. With the development of science and technology in the world, more and more people are aware of agar and agarose, and many people in the industry have seized this opportunity and quickly made use of it, adding agar to various related products, so that the utilization of agar is growing rapidly and the prospects are very good.
3. Agar vs Agarose
Similarities between Agar and Agarose
Same appearance: Agar powder is a white or light yellow powder, and agarose is generally white powder.
The physical properties are the same: They are very easy to decompose into sol in boiling water, insoluble in cold water, but can absorb water and swell into gel-like, and the sol solution is neutral.
Agar and agarose have special gelling properties, especially significant solidity, hysteresis, and easy to absorb water, with a special stabilizing effect.
Difference between Agar and Agarose
1. Different Composition
Agarose is simply a linear polymorph, which is made of alternating galactose connections. Agar, on the other hand, is a polysaccharide extracted from seaweed, and is one of the most widely used seaweed gums in the world.
2. Different Uses
Agar: It is widely used in food industry and is also commonly used as bacterial culture medium. It is also used in chemical industry, medical research, as culture medium and ointment.
Agarose: Widely used in food, medicine, chemical industry, textile, national defense and other fields, according to incomplete statistics, agar vs agarose has more than 1000 kinds of uses, is internationally known as "novel East Asian products".
Recent Posts

We are a biotech company specialized in the research, development and commercialization of innovative and technological food additives hydrocolloids Agar Agar, Carrageenan and Tailor-Made Stabilizer Solutions.
With the extended know-how and experience in the research, application and use of Hydrocolloids, we could provide one-stop-shop customized solutions perfectly matched to the needs of our customers.
Our products cover the needs of the Meat, Dairy, Bakery, Confectionery and other industrial sectors.













